Waterproof Wall Sheathing A Comprehensive Guide
Waterproof wall sheathing is your secret weapon against moisture damage, significantly improving a building’s longevity and energy efficiency. This guide dives deep into the various types, applications, installation techniques, and maintenance practices surrounding this crucial construction material. We’ll explore everything from choosing the right sheathing for your project to understanding relevant building codes, ensuring your project is both effective and compliant. Get ready to become a waterproof wall-sheathing expert!
We’ll cover a wide range of topics, including the different materials available, their properties, and how to choose the best option for your specific needs. We’ll also walk you through the installation process step-by-step, providing practical tips and best practices to ensure a successful and long-lasting installation. We’ll even discuss the environmental impact and cost-effectiveness to help you make informed decisions.
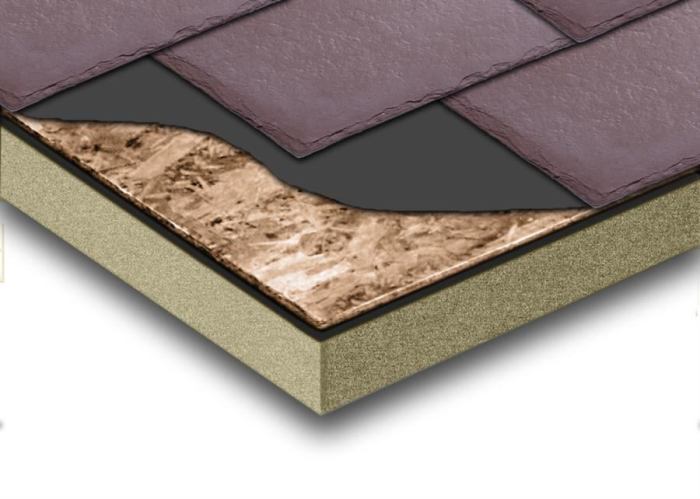
Types of Waterproof Wall Sheathing

Source: co.id
Choosing the right waterproof wall sheathing is crucial for protecting your building from water damage, and ensuring its longevity and structural integrity. Several materials offer varying degrees of waterproofing, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Selecting the appropriate sheathing depends on factors like climate, budget, and the specific needs of the project.
Waterproof Wall Sheathing Materials
The selection of waterproof wall sheathing involves careful consideration of several factors. Understanding the properties and applications of different materials is vital for making an informed decision. The table below summarizes the key characteristics of common types.
| Material | Properties | Applications | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plywood (with waterproof adhesive and sealant) | Strong, relatively inexpensive, and readily available. Requires proper sealing at seams and edges. | Exterior walls, basements, and areas prone to moisture. | Advantages: Cost-effective, good strength. Disadvantages: Requires careful sealing to be truly waterproof; susceptible to rot if improperly sealed. |
| Oriented Strand Board (OSB) (with waterproof adhesive and sealant) | Similar to plywood in strength and cost, but with a more textured surface. Requires proper sealing. | Exterior walls, basements, and areas prone to moisture. | Advantages: Cost-effective, good strength. Disadvantages: Requires careful sealing to be truly waterproof; susceptible to rot if improperly sealed; can be less dimensionally stable than plywood. |
| Cement Board | Highly water-resistant, fire-resistant, and durable. More expensive than plywood or OSB. | Exterior walls, shower surrounds, areas requiring high moisture resistance, and fire protection. | Advantages: Excellent water resistance, fire resistance, and durability. Disadvantages: More expensive, heavier than wood-based sheathing, can be brittle. |
| High-Density Polyurethane Foam Sheathing | Excellent thermal insulation, water-resistant, lightweight. More expensive than traditional sheathing. | Exterior walls in cold climates, energy-efficient buildings. | Advantages: Superior insulation, lightweight, good water resistance. Disadvantages: More expensive, requires specialized fasteners. |
Comparison of Waterproof Wall Sheathing Performance
Plywood and OSB, when properly sealed, offer decent water resistance for many applications. However, their performance is heavily dependent on the quality of the sealant and the care taken during installation. A cement board provides significantly superior water resistance, making it ideal for wet locations. High-density polyurethane foam offers the best thermal performance, reducing energy loss and improving overall building efficiency. Durability varies, with cement board generally being the most durable, followed by plywood and OSB (again, assuming proper sealing and maintenance).
Installation Methods for Waterproof Wall Sheathing
Installation techniques vary depending on the chosen material. Plywood and OSB are typically fastened to wall studs using nails or screws, with all seams and edges carefully sealed with waterproof caulk or sealant. Cement board often requires specialized screws and a waterproof membrane beneath it. High-density polyurethane foam boards are typically attached using adhesive and mechanical fasteners, ensuring a tight seal. In all cases, proper ventilation is crucial to prevent moisture buildup behind the sheathing. Specific tools required include measuring tapes, levels, saws, drills, hammers, and appropriate fasteners for each material. Following the manufacturer’s instructions is essential for optimal performance and warranty validity.
Applications of Waterproof Wall Sheathing

Source: made-in-china.com
Waterproof wall sheathing offers significant advantages in various construction projects, enhancing durability and protecting structures from water damage. Its use extends beyond simply keeping out rain; it’s about creating a robust, long-lasting barrier against moisture intrusion from numerous sources. This leads to reduced maintenance costs and increased lifespan of the building.
The applications of waterproof wall sheathing are diverse, spanning residential and commercial projects alike. Its effectiveness is particularly pronounced in environments susceptible to high humidity or frequent water exposure. Choosing the right sheathing can significantly impact a project’s overall success and longevity.
Residential Applications
In residential construction, waterproof wall sheathing provides crucial protection against moisture-related issues. This is especially important in areas prone to inclement weather or where moisture problems are a common concern.
- Exterior Walls of Houses in Coastal Regions: Salt spray and high humidity are constant threats in coastal areas. Waterproof sheathing acts as a first line of defense against these damaging elements, preventing water penetration and subsequent structural damage.
- Bathrooms and Shower Enclosures: Waterproof sheathing behind tile in bathrooms and shower areas creates a reliable moisture barrier, preventing water from seeping into the wall cavity and causing mold growth or structural damage. This is critical for maintaining a healthy and safe living environment.
- Basements and Crawl Spaces: Basements and crawl spaces are particularly vulnerable to moisture. Waterproof sheathing helps to protect against groundwater seepage and condensation, minimizing the risk of mold and structural problems. It creates a healthier and more energy-efficient space.
- Exterior Walls in High-Rainfall Areas: In regions with heavy rainfall, waterproof sheathing prevents water from penetrating the exterior walls, protecting the building’s structure and interior finishes from water damage.
Commercial Applications
The benefits of waterproof wall sheathing extend to commercial construction, where durability and longevity are paramount. Its use can significantly reduce maintenance and repair costs over the building’s lifetime.
- Exterior Walls of Commercial Buildings: Protecting commercial structures from the elements is crucial for maintaining their value and functionality. Waterproof sheathing helps to prevent water damage and prolong the life of the building’s exterior.
- Swimming Pools and Spas: In environments with high humidity and constant water exposure, such as around swimming pools and spas, waterproof sheathing is essential to prevent water damage to the surrounding structures. It provides a crucial barrier against moisture intrusion.
- Industrial Facilities: Many industrial facilities operate in harsh environments with the potential for water exposure. Waterproof sheathing protects the building from damage and helps maintain a safe and productive work environment.
- Food Processing Plants: Maintaining hygiene is critical in food processing plants. Waterproof sheathing helps prevent moisture buildup and mold growth, contributing to a cleaner and safer environment.
Cost-Effectiveness of Waterproof Sheathing
While the initial cost of waterproof sheathing may be higher than traditional sheathing, the long-term cost savings often outweigh the initial investment. Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario:
Scenario: A 2,000 sq ft single-family home in a coastal region. The cost of traditional sheathing and labor is estimated at $5,000. Waterproof sheathing, including materials and labor, costs approximately $7,000 – a $2,000 difference.
| Material | Traditional Sheathing | Waterproof Sheathing |
|---|---|---|
| Sheathing | $3,000 | $5,000 |
| Labor | $2,000 | $2,000 |
However, consider the potential costs of water damage without waterproof sheathing: mold remediation, structural repairs, and potential health issues could easily exceed $2,000 over the lifespan of the house. The long-term cost savings associated with preventing water damage makes the initial investment in waterproof sheathing a worthwhile consideration, particularly in high-risk environments.
Installation and Best Practices

Source: huaxiajie.com
Installing waterproof wall sheathing correctly is crucial for preventing water damage and ensuring the longevity of your building. Proper installation involves careful planning, precise execution, and attention to detail in every step. Neglecting any aspect can compromise the sheathing’s effectiveness and lead to costly repairs down the line.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Following a methodical approach ensures a successful installation. Each step plays a vital role in creating a robust and watertight barrier.
- Surface Preparation: Begin by thoroughly cleaning the wall surface, and removing any loose debris, dirt, or old coatings. Ensure the surface is level and free from any protrusions that could compromise the sheathing’s adhesion.
- Sheathing Placement: Start installing the sheathing at the bottom of the wall, ensuring proper alignment and overlapping according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Use appropriate fasteners, spaced correctly to prevent damage to the sheathing.
- Fastener Selection and Placement: Choose fasteners appropriate for the sheathing material and wall substrate. Overly long fasteners can penetrate the sheathing, compromising its waterproof integrity. Ensure fasteners are driven straight to avoid splitting the sheathing.
- Seaming and Overlapping: Overlap the sheets of sheathing according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This typically involves a minimum overlap of several inches, ensuring a continuous waterproof barrier.
- Corner and Edge Treatment: Pay special attention to corners and edges. Use appropriate flashing and sealant to create a watertight seal around these vulnerable areas. Improper sealing here is a common source of leaks.
- Quality Control Checks: Regularly inspect the installed sheathing for any gaps, misalignments, or damaged areas. Address any issues immediately to prevent water penetration.
Sealing and Flashing Techniques, Waterproof wall sheathing
Proper sealing and flashing are paramount in preventing water intrusion. These techniques create a continuous barrier, preventing water from penetrating the wall assembly.
Different types of sealants are available, each suited to specific applications and materials. For example, butyl rubber tape is excellent for sealing seams and overlaps, while polyurethane foam sealant can fill gaps and cracks effectively. Silicone caulk is another option, offering good adhesion and flexibility. The choice of sealant depends on the specific requirements of the project and the materials used. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application and curing times.
Flashing, typically made from metal or plastic, is used at critical points like window and door openings, and where the wall meets other building elements. Properly installed flashing directs water away from the wall assembly, preventing it from penetrating the sheathing. Overlapping flashing layers are crucial to ensure complete protection. Incorrect flashing installation can lead to significant water damage.
Handling and Storage Best Practices
Proper handling and storage are crucial to maintaining the integrity of waterproof wall sheathing before and during installation.
Waterproof wall sheathing should be stored in a dry, sheltered location, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Avoid stacking the sheathing too high to prevent damage from crushing or bending. Inspect the sheathing regularly for any signs of damage before installation. Damaged sheathing should be replaced to maintain the integrity of the waterproof barrier. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommended storage guidelines. Protecting the sheathing from the elements prevents premature degradation and ensures its effectiveness upon installation.
Maintenance and Longevity

Source: 99.co
Proper maintenance is key to maximizing the lifespan and performance of your waterproof wall sheathing. Regular inspection and simple cleaning can prevent minor issues from escalating into costly repairs, ensuring your building remains protected and energy-efficient for years to come. Neglecting maintenance, on the other hand, can lead to premature degradation and compromise the sheathing’s waterproof integrity.
Regular inspection and cleaning are crucial first steps in maintaining waterproof wall sheathing. Dirt, debris, and mold can accumulate on the surface, potentially trapping moisture and damaging the protective layer. This can lead to warping, cracking, and ultimately, water penetration. Addressing these issues promptly prevents significant damage and extends the life of the sheathing.
Environmental Impact on Longevity
Exposure to harsh environmental conditions significantly impacts the longevity of waterproof wall sheathing. Prolonged UV exposure from sunlight can degrade the material’s polymers, causing them to become brittle and crack. This is particularly true for sheathing materials that lack UV stabilizers. Similarly, extreme temperature fluctuations, especially frequent cycles of freezing and thawing, can cause stress on the sheathing, leading to expansion and contraction that can weaken its structural integrity and compromise its water resistance. Coastal areas, experiencing both intense sun and salty air, experience accelerated degradation. For instance, a building in a Florida coastal city might require more frequent inspections and potential repairs compared to one in a more temperate climate.
Maintenance Procedures
Maintaining waterproof wall sheathing involves a straightforward routine. Regular visual inspections, at least annually, should be performed to check for any signs of damage, such as cracks, discoloration, or loose seams. Cleaning the sheathing with a mild detergent and water can remove dirt and debris. Pressure washing should be avoided as it can damage the surface. For areas with heavy mold growth, a specialized cleaning solution might be necessary. Promptly addressing any discovered issues, such as repairing minor cracks with appropriate sealant, prevents larger problems from developing. For example, a small crack left unattended could allow water penetration, leading to extensive damage to the underlying wall structure and potentially mold growth.
Impact on Energy Efficiency
Proper installation and consistent maintenance of waterproof wall sheathing significantly contribute to a building’s energy efficiency. A well-maintained waterproof barrier prevents moisture from penetrating the walls, reducing the risk of mold growth and improving indoor air quality. Moisture intrusion can lead to thermal bridging, where heat escapes more readily through damp areas, increasing energy consumption for heating and cooling. By preventing moisture penetration, the sheathing maintains the insulating properties of the wall assembly, leading to a more stable and energy-efficient building. For instance, a building with properly maintained waterproof sheathing might require 10-15% less energy for climate control compared to one with compromised sheathing. This translates to lower energy bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
Environmental Considerations: Waterproof Wall Sheathing

Source: pmjmosaic.com
Choosing waterproof wall sheathing involves more than just functionality; it also has significant environmental implications throughout its lifecycle, from manufacturing to disposal. Understanding these impacts helps us make informed decisions that minimize our environmental footprint. This section examines the environmental impact of various sheathing types, explores eco-friendly alternatives, and discusses end-of-life management options.
The environmental impact of waterproof wall sheathing varies greatly depending on the material used. Factors such as energy consumption during manufacturing, the sourcing of raw materials, and the potential for recycling all play a role.
Environmental Impacts of Different Waterproof Wall Sheathing Types
Let’s look at the environmental impact of some common waterproof wall sheathing materials. It’s crucial to remember that these impacts can vary depending on the specific manufacturing processes and sourcing of materials.
- Cement Board: Manufacturing cement board is energy-intensive, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. The extraction and processing of raw materials like clay and limestone also have environmental consequences, including habitat disruption and dust pollution. Disposal can contribute to landfill volume. Cement boards are generally not easily recyclable.
- Plastic-Based Sheathing (e.g., PVC, HDPE): The production of plastic sheathing relies heavily on fossil fuels, leading to significant carbon emissions. These materials are not biodegradable and contribute to plastic waste in landfills. Recycling options are limited for many types of plastic sheathing, although some advancements are being made in this area.
- Metal Sheathing (e.g., Aluminum, Zinc): Metal sheathing production requires significant energy, and aluminum production, in particular, is energy-intensive. Metal sheathing is often recyclable, but the recycling process itself consumes energy. Depending on the source of the metal, mining activities can have environmental impacts.
- Wood-Based Sheathing (e.g., treated lumber): Wood-based sheathing, especially treated lumber, can have environmental impacts related to deforestation, the use of chemical preservatives (which can pollute waterways), and transportation. However, wood is a renewable resource, and properly managed forestry practices can mitigate some of these impacts. Disposal can be easier than other materials, with some potential for reuse or repurposing.
Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Options
Fortunately, more eco-friendly and sustainable options for waterproof wall sheathing are becoming increasingly available. These materials aim to reduce environmental impact throughout their lifecycle.
- Recycled Content Sheathing: Some manufacturers are incorporating recycled materials into their sheathing products, reducing reliance on virgin resources and diverting waste from landfills. Look for products with high percentages of recycled content.
- Sheathing Made from Rapidly Renewable Resources: Materials derived from rapidly renewable resources, such as bamboo or certain fast-growing tree species, offer a more sustainable alternative to traditional lumber.
- Sheathing with Low-VOC Coatings: Choosing sheathing with low-volatile organic compound (VOC) coatings minimizes the release of harmful chemicals into the air during and after installation.
Recyclability and Reuse Potential
The recyclability and reuse potential of waterproof wall sheathing varies significantly by material. Proper end-of-life management is essential to minimize environmental impact.
- Metal Sheathing: Metal sheathing generally has good recyclability. Check with local recycling centers for proper disposal and recycling procedures.
- Wood-Based Sheathing: Depending on the treatment, wood sheathing may be suitable for reuse or repurposing in other applications. Untreated wood can often be used for less demanding projects.
- Plastic and Cement-Based Sheathing: Recycling options are limited for these materials, and proper disposal in designated landfills is usually necessary.
Code Compliance and Regulations

Source: cortina-panel.com
Navigating building codes and regulations for waterproof wall sheathing can seem daunting, but understanding the basics is crucial for a successful and legally sound project. These regulations vary significantly depending on your location, influenced by factors like climate, seismic activity, and local building practices. Ignoring these codes can lead to costly repairs, project delays, and even legal repercussions.
Building codes related to waterproof wall sheathing primarily focus on moisture control, structural integrity, and fire safety. They often specify minimum requirements for the type of sheathing allowed, its installation methods, and the necessary vapor barriers or drainage planes. These requirements are designed to protect the building’s structure from water damage, ensuring its longevity and occupant safety. For example, coastal regions might have stricter requirements due to the increased risk of water damage from storms and high humidity. Similarly, areas prone to earthquakes may have specific guidelines to ensure the sheathing contributes to the building’s overall seismic resilience.
Determining Applicable Building Codes
Identifying the specific building codes applicable to your project is the first and most critical step. This involves checking with your local building department or referring to the model codes adopted in your region. Common model codes include the International Building Code (IBC), the International Residential Code (IRC), and local amendments or additions. These codes often provide detailed specifications for water-resistive barriers, including acceptable materials, installation techniques, and overlap requirements. For example, the IBC might specify minimum requirements for the water resistance of the sheathing, while the IRC might offer more specific guidance for residential construction. Ignoring these specifications can result in the rejection of building permits and subsequent project delays.
Ensuring Compliance During Selection and Installation
Choosing the right waterproof wall sheathing involves careful consideration of the local building codes. This means selecting a material that meets or exceeds the specified requirements for water resistance, structural integrity, and fire safety. The chosen material’s performance characteristics should be verifiable through testing and certifications, often documented in product datasheets and compliance reports. Furthermore, installation must strictly adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions and the relevant building code provisions. This includes proper fastening techniques, ensuring sufficient overlap of sheathing panels, and correct integration with other building components like flashing and vapor barriers. Deviation from these guidelines could compromise the sheathing’s effectiveness and potentially lead to code violations.
Examples of Common Code Violations and Consequences
Failure to properly install a water-resistive barrier, such as inadequate overlapping of sheathing panels or incorrect flashing around windows and doors, is a frequent code violation. This can lead to water intrusion, causing mold growth, structural damage, and health problems for occupants. Another common violation is the use of unsuitable materials – employing sheathing not rated for the specific climatic conditions or lacking necessary certifications. This could result in premature failure of the wall system, leading to expensive repairs and potential legal liabilities. Finally, neglecting to properly seal penetrations in the sheathing, such as for pipes or electrical conduits, can create pathways for water to enter the building’s structure, resulting in similar issues to those described above. The consequences of these violations can range from project delays and increased construction costs to legal action and fines from building inspectors.
Last Point

Source: co.id
Mastering the art of waterproof wall sheathing installation is key to creating durable, energy-efficient, and safe structures. From understanding the nuances of different materials to implementing proper installation and maintenance techniques, this guide equips you with the knowledge to tackle any project with confidence. Remember, investing in quality waterproof wall sheathing is an investment in the long-term health and value of your building. By following the best practices Artikeld here, you can ensure a successful project that stands the test of time and the elements.