Pro Exterior Siding A Homeowners Guide
Pro exterior siding transforms houses into homes, offering a blend of aesthetics and protection. This guide dives into the world of siding, exploring various materials like wood, vinyl, fiber cement, and metal—each with its unique charm, durability, and cost implications. We’ll cover everything from installation techniques and maintenance tips to budgeting and environmental considerations, empowering you to make informed decisions for your home’s exterior.
From choosing the right material to understanding the installation process and long-term maintenance, we’ll walk you through each step, providing practical advice and visual aids to make your siding project a success. We’ll also address the financial aspects, helping you create a realistic budget and find reliable contractors. Finally, we’ll explore the environmental impact of different siding choices, enabling you to select sustainable options.
Types of Pro Exterior Siding
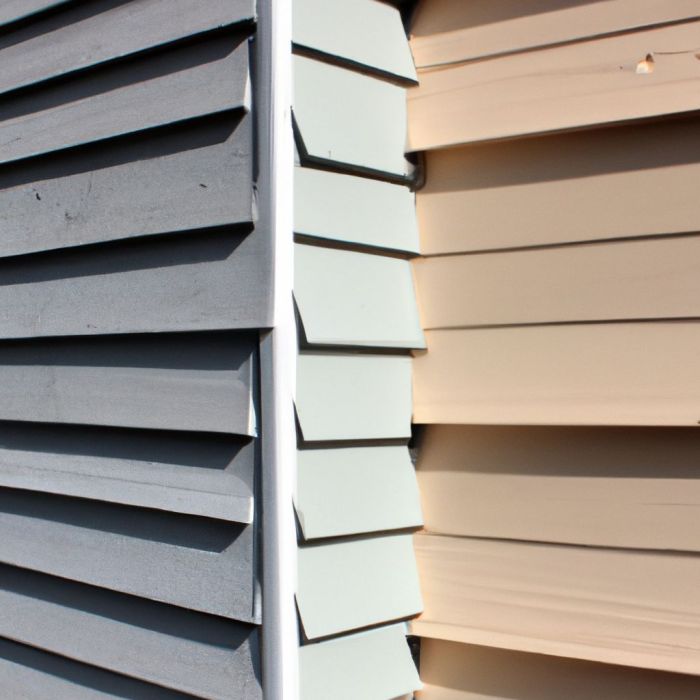

Source: autoblogging.ai
Choosing the right exterior siding is a crucial decision that impacts your home’s curb appeal, durability, and long-term maintenance. This section will explore various popular siding materials, comparing their characteristics, aesthetics, installation, and overall cost-effectiveness.
Popular Exterior Siding Materials
Several materials dominate the exterior siding market, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is key to making an informed choice.
- Vinyl Siding: Known for its affordability and low maintenance, vinyl is a popular choice. It’s relatively easy to install, resists rot and insect damage, and comes in a wide variety of colors and styles. However, it can be susceptible to damage from impacts and extreme temperatures, and it doesn’t offer the same aesthetic appeal as some other materials. Its lifespan is typically 20-30 years.
- Fiber Cement Siding: A composite material made from cement, cellulose fibers, and sand, fiber cement siding boasts exceptional durability and fire resistance. It mimics the look of wood but requires more maintenance than vinyl, needing occasional painting. Installation is more complex than vinyl, requiring specialized tools and expertise. Its lifespan is generally 50 years or more.
- Wood Siding: Offering a classic, natural aesthetic, wood siding provides a warm and inviting look. However, it requires significant maintenance, including regular painting or staining, and is susceptible to rot, insect infestation, and fire damage. Different wood types (e.g., cedar, and redwood) have varying lifespans and maintenance needs. Proper installation is critical to prevent water damage. Lifespan varies greatly depending on wood type and maintenance, ranging from 20-50+ years.
- Metal Siding: Typically made from aluminum or steel, metal siding is incredibly durable, fire-resistant, and low-maintenance. It’s also resistant to pests and rot. However, it can be susceptible to dents and scratches, and its appearance may not appeal to everyone. It can also be more expensive than vinyl siding. Lifespan is generally 50+ years.
Aesthetic Appeal of Different Siding Materials
The visual impact of siding significantly influences a home’s overall appearance. Vinyl siding offers a wide range of colors and styles, mimicking the look of wood or other materials, but sometimes appearing less realistic. Fiber cement provides a more authentic wood-like appearance, offering a clean, modern, or traditional look depending on the style chosen. Wood siding offers unparalleled natural beauty and texture, though this requires careful selection and maintenance to retain its appeal. Metal siding’s appearance varies greatly depending on the finish and style; it can have a modern, industrial, or even rustic look, depending on the design.
Installation Methods and Considerations
Each siding type requires specific installation techniques. Vinyl siding is generally installed using a nailing system, requiring careful attention to overlap and alignment. Fiber cement siding is often installed using nails or screws, requiring precise measurements and cuts to ensure a proper fit. Wood siding installation is more labor-intensive, involving careful planning and attention to detail to prevent water penetration. Metal siding is usually installed using a similar system to vinyl, but the materials and tools required are different. All types require proper flashing and sealing around windows and doors to prevent water intrusion. Improper installation can lead to significant problems, including water damage, rot, and reduced lifespan.
Siding Material Comparison
| Siding Type | Lifespan (Years) | Cost-Effectiveness (Low/Medium/High) | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | 20-30 | Low | Low |
| Fiber Cement | 50+ | Medium | Medium |
| Wood | 20-50+ | Medium-High | High |
| Metal | 50+ | High | Low |
Pro Exterior Siding Installation

Source: f-cdn.com
Professional exterior siding installation is a multi-step process requiring precision and attention to detail. Proper preparation and execution are crucial for a long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing, and weather-resistant exterior. This section Articulates the key steps involved in a typical installation, focusing on best practices and essential tools.
Wall Surface Preparation
Before any siding goes up, the wall needs to be thoroughly prepared. This involves several key steps to ensure a smooth, even surface for the siding to adhere to. A poorly prepared surface can lead to problems later, including uneven siding, gaps, and potential water damage. First, remove any existing siding or damaged materials. Then, repair any cracks or holes in the underlying sheathing using appropriate patching materials. Next, ensure the sheathing is properly fastened and leveled. Finally, apply a weather-resistant barrier, such as house wrap, to protect the wall from moisture. This is especially important in areas prone to high winds and rain. Remember to overlap the house wrap seams properly to prevent water penetration.
Tools and Equipment
Professional siding installation requires specialized tools and equipment for efficient and accurate work. These tools ensure proper cuts, fastening, and overall quality of the installation. Essential tools include a measuring tape, level, chalk line, circular saw, miter saw (for angled cuts), utility knife, hammer, nail gun (often preferred for speed and efficiency), safety glasses, work gloves, and a ladder (or scaffolding for taller buildings). Depending on the siding material, you may also need specific tools like a heat gun (for vinyl siding) or specialized fasteners. Remember, safety is paramount. Always use appropriate safety equipment.
Vinyl Siding Installation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Vinyl siding is a popular choice for its affordability and low maintenance. Installing it correctly ensures a beautiful and durable exterior. The following steps provide a detailed guide to professional vinyl siding installation.
- Starting Point: Begin at a corner of the house, usually the most visible one. Install the J-channel, which provides a neat finish at the edges and allows for expansion and contraction of the siding. This is often installed vertically, forming a channel into which the first siding piece will be inserted. Imagine the J-channel as a small, upside-down ‘J’ shaped piece of metal. It’s essential for a clean, professional look.
- First Piece: Carefully measure and cut the first vinyl siding piece to fit. It will usually be a full-length piece and will be slid into the J-channel, ensuring it’s flush with the top and bottom. The bottom edge should rest on the foundation or a starting strip, depending on the installation details. Ensure it’s properly aligned before fastening.
- Fastening: Use appropriate fasteners, typically nails or staples, to secure the siding to the wall. Avoid driving nails all the way through; leave a small gap for expansion. This is vital to prevent warping or damage caused by temperature fluctuations. The nails should be placed near the top of the siding piece, hidden beneath the overlapping piece above.
- Overlapping Pieces: Subsequent siding pieces overlap the previously installed pieces. The bottom edge of each new piece slides under the top edge of the previous one. This overlapping creates a weather-resistant seal and a visually appealing finish. Always ensure proper overlap to prevent water penetration.
- Cutting and Fitting: Around windows and doors, you’ll need to measure carefully and cut the siding to fit. Use a miter saw for accurate angled cuts. Vinyl siding can be easily cut with a sharp utility knife or a circular saw. Use a heat gun to gently soften the vinyl for easier bending or shaping around corners or difficult areas.
- Finishing: Once the main siding is installed, install the J-channel or other finishing pieces around windows, doors, and corners to complete the look. Pay attention to detail to ensure a clean, professional finish. This final step is crucial for a weathertight and visually appealing installation.
Maintenance and Repair of Pro Exterior Siding

Source: totalhomekc.com
Proper maintenance is key to extending the lifespan of your exterior siding and maintaining your home’s curb appeal. Regular cleaning and prompt repairs prevent small problems from escalating into costly replacements. Different siding materials require slightly different care, so understanding your siding type is crucial.
Cleaning and Maintaining Different Siding Types
Cleaning methods vary depending on the siding material. Vinyl siding is generally easy to clean; a simple wash with soap and water, using a soft-bristled brush, is often sufficient. For tougher stains, a pressure washer can be effective, but use caution to avoid damaging the siding; maintain a safe distance and use a low-pressure setting. Wood siding requires more care. Regularly inspect for signs of rot or insect infestation. Cleaning typically involves a gentle scrub with a solution of mild detergent and water, followed by rinsing. Never use harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners on wood siding. Fiber cement siding is durable and relatively low maintenance. Cleaning usually involves washing with soap and water, similar to vinyl. However, be sure to avoid prolonged exposure to moisture to prevent water damage. For all siding types, it’s recommended to clean from top to bottom to prevent streaks.
Common Siding Problems and Their Causes
Several issues can affect exterior siding. Cracking in vinyl siding can be caused by impact damage, extreme temperature fluctuations, or improper installation. Fading is common, particularly in sun-exposed areas, and is often due to prolonged UV exposure. Water damage, leading to rot or mold, can result from gaps in caulking, damaged flashing, or inadequate drainage around the foundation. Wood siding is susceptible to rot and insect infestation if not properly maintained. Fiber cement siding is less prone to these problems but can still crack or chip from impact.
Repairing Minor Siding Damage
Minor repairs are often manageable with DIY skills. Replacing damaged vinyl siding panels usually involves removing the damaged panel and installing a new one, securing it with appropriate fasteners. Caulking gaps around windows, doors, and other areas is essential to prevent water intrusion. For wood siding, minor repairs may involve filling small cracks or holes with wood filler and then repainting. Larger areas of damaged wood siding may require panel replacement. Damaged fiber cement siding panels may need to be replaced, carefully matching the color and texture of existing panels. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific repair procedures.
Annual Siding Inspection and Maintenance Checklist
A yearly inspection is recommended to catch small problems before they become major repairs.
- Visual Inspection: Check for cracks, chips, fading, loose panels, or signs of water damage.
- Caulk Inspection: Examine caulking around windows, doors, and other areas for cracks or gaps. Recaulk as needed.
- Drainage Check: Ensure proper drainage around the foundation to prevent water accumulation against the siding.
- Cleaning: Wash the siding with soap and water, using appropriate methods for the siding material.
- Insect Inspection (Wood Siding): Look for signs of insect infestation, such as holes or insect droppings.
- Flashing Inspection: Check the condition of flashing around windows, doors, and other areas to prevent water leakage.
Regular maintenance, including a yearly inspection and cleaning, will significantly increase the life of your exterior siding and protect your home’s investment.
Cost Considerations for Pro Exterior Siding

Source: mydecorative.com
Choosing new exterior siding is a significant investment, impacting both your home’s curb appeal and its long-term value. Understanding the cost factors involved will help you make informed decisions and avoid unpleasant surprises during the project. This section breaks down the key cost components and offers strategies for budgeting effectively.
Material Costs
The type of siding you choose significantly impacts the overall cost. Vinyl siding is generally the most affordable option, offering a balance of durability and price. Fiber cement siding provides superior durability and fire resistance but comes with a higher price tag. Wood siding, while aesthetically pleasing, is the most expensive and requires more maintenance. Metal siding, such as aluminum or steel, falls somewhere in between, offering good durability and a relatively moderate price. The cost per square foot varies greatly depending on the material’s quality, features (e.g., texture, color), and the supplier. For example, a basic vinyl siding might cost $3-$6 per square foot, while high-end fiber cement could reach $10-$20 or more. Always get multiple quotes from different suppliers to compare prices and options.
Labor Costs
Labor costs represent a substantial portion of the overall project expense. The complexity of the job, the size of your house, and the contractor’s experience all influence labor costs. A simple siding replacement on a smaller house might require less labor, while a more intricate project involving significant repairs or unique architectural features will cost more. Expect to pay anywhere from $2 to $8 or more per square foot for labor, depending on these factors. Getting multiple bids from different contractors allows you to compare labor rates and assess their value proposition.
Permits and Inspections
Securing the necessary permits and passing inspections are crucial for a legally compliant and safe installation. Permit fees vary depending on your location and the scope of the project. These costs should be factored into your budget from the outset. In some areas, inspections might also incur additional fees. It’s best to inquire about permit and inspection costs early in the planning phase to avoid unexpected expenses.
Cost-Effectiveness of Different Siding Options
While initial costs vary widely, it’s essential to consider the long-term cost-effectiveness of different siding materials. Vinyl siding, though inexpensive upfront, may require replacement sooner than more durable options like fiber cement or metal. Fiber cement, while more expensive initially, boasts a longer lifespan and requires less maintenance, potentially offsetting the higher initial investment over time. Wood siding, despite its beauty, demands significant ongoing maintenance, making its long-term cost potentially higher than other choices. Therefore, consider the lifespan, maintenance requirements, and potential repair costs when evaluating the overall cost-effectiveness of each option. For example, a 20-year lifespan for vinyl siding might cost less per year than a 50-year lifespan for fiber cement if maintenance costs for the vinyl are significantly higher.
Finding Reputable and Affordable Siding Contractors, Pro exterior siding
Finding a reliable and reasonably priced contractor is key to a successful project. Check online reviews, request references, and verify licensing and insurance. Get at least three written bids from different contractors, comparing not just the price but also the details of their proposals, including materials, labor, and warranties. Don’t hesitate to ask questions about their experience, processes, and how they handle potential problems. Choosing a contractor based solely on the lowest price can be risky; prioritize experience and reputation to ensure a quality installation.
Creating a Realistic Budget
Start by obtaining accurate measurements of your home’s exterior surface area. Then, get detailed quotes from multiple contractors, including material costs, labor costs, permit fees, and any other anticipated expenses. Add a contingency buffer of 10-20% to account for unexpected costs or potential changes during the project. A realistic budget will allow you to make informed decisions about your siding choice and avoid financial strain during the project. For example, if the estimated cost is $10,000, adding a 15% contingency would bring the total budget to $11,500. This approach helps prevent financial surprises and ensures a smoother project execution.
Environmental Impact of Pro Exterior Siding

Source: exteriorarmor.com
Choosing exterior siding involves more than just aesthetics and cost; it significantly impacts the environment. From manufacturing to disposal, each siding material carries an environmental footprint. Understanding this impact helps homeowners make informed, sustainable choices. This section explores the environmental considerations of various siding options, emphasizing energy efficiency and eco-friendly alternatives.
Manufacturing Processes and Disposal of Different Siding Materials
The manufacturing process of different siding materials varies widely, resulting in different levels of environmental impact. For example, vinyl siding, while often affordable, requires significant energy input during its production and releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Wood siding, depending on its source and treatment, can have a lower carbon footprint if sourced sustainably, but its manufacturing may involve the use of chemicals and preservatives. Metal siding, primarily aluminum or steel, requires substantial energy for mining and processing the raw materials, although recycled content can lessen this impact. Fiber cement siding, a composite material, involves a manufacturing process that produces waste, but its durability can offset this over its lifetime. Finally, the disposal of each material presents unique challenges; vinyl and some composite sidings are not easily recyclable, while wood can be repurposed or composted under certain circumstances. Proper disposal methods are crucial to minimizing landfill contributions and potential environmental harm.
Energy Efficiency of Different Siding Options
Exterior siding plays a crucial role in a home’s energy efficiency. Materials with high R-values (a measure of thermal resistance) provide better insulation, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. For instance, fiber cement siding often offers superior insulation compared to vinyl, leading to lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint over the siding’s lifespan. Proper installation of any siding type, including the use of appropriate insulation behind the siding, is also vital for maximizing energy efficiency. Homes with well-insulated siding can experience a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, benefiting both the homeowner and the environment. A home in a colder climate, for instance, with properly installed fiber cement siding and adequate insulation, might see a 15-20% reduction in heating costs compared to a home with less efficient siding.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Siding Choices
Several siding options offer more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives. Recycled materials, such as recycled plastic in composite sidings or recycled aluminum in metal sidings, reduce the demand for virgin resources. Siding made from rapidly renewable resources, such as bamboo, offers a lower carbon footprint compared to materials derived from slow-growing trees. Furthermore, choosing locally sourced wood siding minimizes transportation emissions. When considering sustainable options, it’s important to look for certifications like Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification for wood products, ensuring responsible forestry practices. Choosing a durable siding that lasts longer also reduces the frequency of replacement and its associated environmental impact. A longer-lasting siding reduces the need for frequent replacements and associated manufacturing and disposal impacts.
Environmentally Conscious Practices Related to Siding Installation and Disposal
Careful consideration of environmental impacts should extend beyond material selection to installation and disposal.
- Properly dispose of old siding materials according to local regulations. Many communities offer recycling programs for specific materials, or you might find companies specializing in siding removal and responsible disposal.
- Minimize waste during installation by accurately measuring and cutting materials. Repurpose or recycle leftover materials whenever possible.
- Use environmentally friendly cleaning products during installation and maintenance to avoid water contamination.
- Choose installers committed to sustainable practices, including waste reduction and proper disposal methods.
- Consider the embodied energy of the siding and the overall life-cycle assessment when making your selection.
Design Considerations for Pro Exterior Siding

Source: harborexports.com
Choosing the right exterior siding isn’t just about protection; it’s a key design element that significantly impacts your home’s curb appeal and overall aesthetic. The color, texture, and pattern of your siding can dramatically alter the look and feel of your house, enhancing its architectural style and creating a welcoming atmosphere. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial for achieving a visually stunning and cohesive exterior.
The interplay between siding and architectural style is paramount. The right siding choice can either complement the existing architectural features or completely transform the home’s character. For example, a traditional Victorian home might be beautifully enhanced with clapboard siding in a classic color palette, while a modern minimalist house might benefit from sleek, linear siding in a neutral tone. The texture of the siding also plays a vital role; smooth surfaces convey a sense of modernity, while rougher textures add rustic charm.
Aesthetic Impact of Siding Colors and Textures
Siding color significantly influences the overall mood and feel of a home. Light colors, such as creamy whites and soft grays, create a sense of spaciousness and airiness, making smaller homes appear larger. Darker colors, such as deep blues and browns, lend a sense of sophistication and drama, especially when used on larger homes. Texture adds another layer of visual interest. For instance, wood-grain siding provides a natural, warm feel, while smooth vinyl siding offers a clean, contemporary look. The interplay of color and texture creates a dynamic visual effect that can be tailored to match personal preferences and architectural style.
Siding and Architectural Style Enhancement
The choice of siding should harmonize with the architectural style of the house. A Craftsman-style home might look best with horizontal wood siding or a similar textured alternative, while a farmhouse might benefit from vertical board and batten siding. A contemporary home might utilize large format panels or sleek, metal-clad siding. The goal is to create a cohesive and visually pleasing exterior that doesn’t clash with the existing architectural details. Using siding that complements the existing features, such as window frames, rooflines, and landscaping, will result in a more polished and unified look.
Examples of Creative Siding Designs and Patterns
Beyond basic applications, siding can be used creatively to add visual interest and personality to a home. Consider incorporating different siding materials or colors in a strategic pattern, such as alternating dark and light panels to create a visually striking effect. Accent walls can also be created using a contrasting color or texture, drawing the eye to a specific feature of the house. The use of architectural details, such as trim, molding, and decorative accents, further enhances the overall aesthetic. For instance, using contrasting colored trim around windows and doors can frame these elements and draw attention to them.
Three Hypothetical Exterior Siding Schemes
Let’s imagine three different siding schemes for a hypothetical two-story colonial-style home:
Scheme 1: Classic Elegance: This scheme features traditional clapboard siding in a warm, creamy white. Dark gray shutters and a dark gray front door provide a striking contrast, while white trim around the windows and along the roofline accentuates the architectural details. The overall effect is one of timeless elegance and understated sophistication. The landscaping would include lush green lawns and mature shrubs, complementing the neutral color palette.
Scheme 2: Modern Farmhouse Charm: This scheme utilizes vertical board and batten siding in a soft gray hue. The siding’s texture adds rustic charm, while the gray color provides a neutral backdrop. A bright white front door and black window frames create a bold contrast, enhancing the home’s modern farmhouse aesthetic. The landscaping incorporates elements like wildflowers, stone pathways, and a picket fence.
Scheme 3: Coastal Contemporary: This scheme showcases smooth, light gray fiber cement siding with subtle texture. The clean lines of the siding complement the home’s colonial style while lending a contemporary feel. White trim, blue shutters, and a bright blue front door create a cheerful, coastal vibe. The landscaping incorporates beach grasses, sandy-colored stones, and perhaps a small, carefully placed patio.
Final Conclusion

Source: calgarysidingsolutions.com
Ultimately, selecting the right pro exterior siding involves careful consideration of aesthetics, durability, budget, and environmental impact. This guide has equipped you with the knowledge to navigate these factors confidently. Remember to prioritize thorough research, choose reputable contractors, and meticulously plan your project for a beautiful and long-lasting result. Your home’s exterior is its first impression—make it count!