ADU Exterior Design Style & Functionality
ADU exterior design is more than just slapping on some siding; it’s about creating a space that’s both beautiful and functional. This guide dives into the key aspects of designing your ADU’s exterior, from choosing the right architectural style and materials to navigating building codes and budgeting effectively. We’ll explore current trends, sustainable design options, and the importance of integrating your ADU seamlessly with your main house and the surrounding landscape. Get ready to transform your ADU from a simple structure into a stunning addition to your property!
We’ll cover everything from understanding popular architectural styles like Craftsman, Modern, and Farmhouse, to selecting cost-effective yet aesthetically pleasing materials. Learn how lighting, landscaping, and even window styles can dramatically impact your ADU’s curb appeal and energy efficiency. We’ll also walk you through the permitting process and offer practical tips for budgeting and managing the costs involved in your ADU exterior project. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence to create an ADU exterior that you’ll love for years to come.
Understanding Adu Exterior Design Trends

Source: theotexture.com
A well-designed Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) exterior significantly impacts curb appeal and property value. Staying current with design trends ensures your ADU blends seamlessly with its surroundings while maintaining a modern and attractive aesthetic. This section explores popular styles, materials, and design examples to inspire your ADU project.
Popular ADU Exterior Styles
Current trends favor ADU exteriors that complement the main house while possessing their distinct character. Clean lines, sustainable materials, and thoughtful landscaping are key elements. Modern farmhouse styles, with their blend of rustic and contemporary elements, remain highly popular, alongside sleek contemporary designs and more traditional styles adapted for modern sensibilities. The choice ultimately depends on the existing architectural style of the main house and the overall neighborhood aesthetic.
Three Distinct Architectural Styles for ADU Exteriors
- Modern Farmhouse: This style features a blend of rustic and contemporary elements. Think clapboard siding, large windows, a gable roof, and a porch with simple detailing. Materials might include wood, stone accents, and metal roofing. The overall effect is charming and inviting, yet sophisticated.
- Contemporary: Contemporary ADUs emphasize clean lines, geometric shapes, and minimalist detailing. Materials like stucco, metal siding, and large expanses of glass are common. The focus is on functionality and a sleek, modern aesthetic. Color palettes tend to be neutral and sophisticated, using shades of gray, white, and black.
- Traditional: Traditional styles adapt classic architectural elements for a modern context. This might involve using traditional materials like brick or shingle siding but with updated proportions and details. Elements such as dormers, symmetrical facades, and detailed trim work can be incorporated, but with a simplified approach to avoid an overly ornate look. The result is a timeless and elegant design.
Comparison of Exterior Materials
The choice of exterior materials significantly impacts the ADU’s aesthetic, durability, and maintenance requirements.
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Brick | Durable, fire-resistant, low maintenance | Expensive, can be heavy, limited color options |
| Siding (Vinyl, Fiber Cement, Wood) | Variety of colors and styles, relatively affordable (vinyl), durable (fiber cement) | Can be damaged by impact (vinyl), requires more maintenance (wood), can fade (vinyl) |
| Stone | Durable, natural look, high-end aesthetic | Expensive, heavy, requires skilled installation |
Three ADU Exterior Facade Designs, Adu exterior design
- Design 1 (Modern Farmhouse): Imagine a charming ADU with white clapboard siding, a dark gray gable roof, and black framed windows. A small covered porch with a simple wooden railing adds to the inviting appeal. Stone accents around the base and near the entrance provide visual interest and a touch of rustic charm. This design uses a combination of wood, stone, and metal roofing.
- Design 2 (Contemporary): Picture a sleek ADU with smooth gray stucco walls, large floor-to-ceiling windows, and a flat roof. A recessed entryway with a metal canopy adds a modern touch. The overall aesthetic is clean, minimalist, and sophisticated, utilizing mainly stucco and metal accents.
- Design 3 (Traditional with a Modern Twist): Envision a traditional style ADU with a brick facade, but with updated window proportions and a simplified trim design. A slightly pitched roof with dark gray shingles completes the look. This design focuses on a classic brick exterior with subtle modern touches in the detailing, emphasizing simplicity and clean lines within a traditional framework.
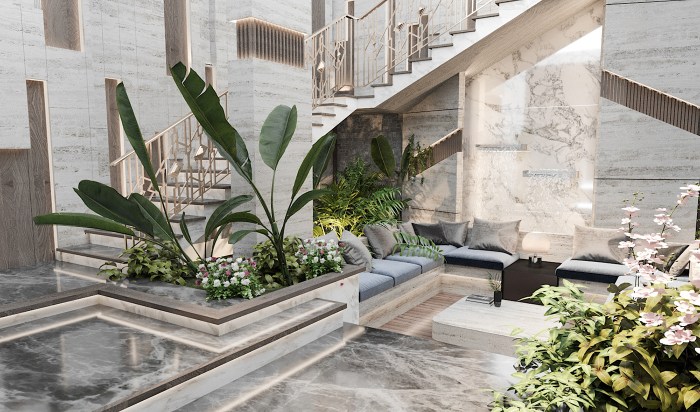
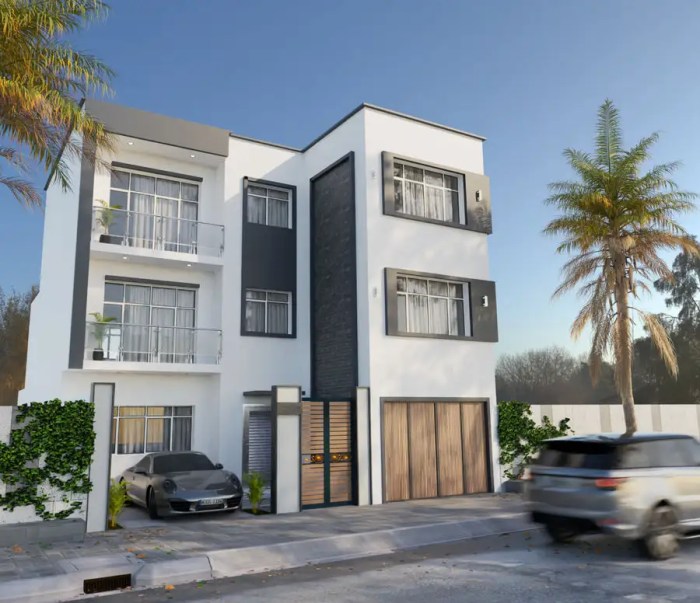
Adu Exterior Design Elements

Source: f-cdn.com
Creating a stunning and functional adu exterior involves careful consideration of several key elements. The goal is to seamlessly blend the ad’s design with the main house and the surrounding landscape while maximizing curb appeal and energy efficiency. This requires a thoughtful approach to materials, lighting, landscaping, and window selection.
Adu Exterior Design Integration with Main House Style
Harmonizing the aNaidu’sexterior with the main house is crucial for maintaining a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing property. If the main house is a traditional Victorian, for example, the adu should reflect similar architectural details, such as ornate trim, gables, or bay windows. Conversely, a modern main house would pair well with a contemporary adu featuring clean lines, minimalist details, and possibly a flat roof. Consider using similar materials, color palettes, and architectural styles to create a unified look. Even subtle similarities, like using the same type of siding or matching brickwork, can make a significant difference.
Lighting to Enhance Adu Curb Appeal
Strategic lighting can dramatically improve an ad’s nighttime appearance and enhance its overall curb appeal. Path lighting guides visitors safely to the entrance, while uplighting accentuates architectural features like columns or dormers. Recessed lighting in eaves or soffits provides soft, ambient illumination, while spotlights highlight landscaping elements like trees or flowerbeds. Consider using energy-efficient LED lighting to minimize energy consumption and operational costs. Warm-toned lighting generally creates a welcoming atmosphere, while cooler tones can provide a more modern feel.
Landscaping to Complement Adu Exterior Design
Landscaping plays a vital role in softening the aNaidu’sexterior and integrating it into the overall landscape design. Careful plant selection can create a visually appealing buffer between the adu and the main house or street. Low-maintenance plants, such as drought-tolerant shrubs or groundcovers, are ideal for minimizing upkeep. For example, using native plants can create a natural and sustainable look, while incorporating flowering plants adds bursts of color throughout the year. Hardscaping elements, like pathways, patios, and retaining walls, can further enhance the adult’s aesthetic appeal and functionality. A small patio adjacent to the adu could create a private outdoor space for relaxation or entertaining.
Impact of Window Styles on Adu Aesthetics and Energy Efficiency
The choice of window style significantly impacts both the adu’s aesthetics and its energy efficiency. Different styles offer unique visual characteristics and varying levels of insulation.
| Window Style | Aesthetic Impact | Energy Efficiency | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casement | Clean lines, modern feel; can be incorporated into various styles | Good; tight seal when closed | Excellent for ventilation due to crank-out design. |
| Bay | Adds architectural interest, expands interior space | Can be good or poor depending on construction and glazing | May require more energy for heating/cooling due to increased surface area. |
| Double-Hung | Classic, versatile style suitable for most architectural styles | Moderate; can be improved with weatherstripping and efficient glazing | Easy to clean and maintain. |
| Fixed | Modern, minimalist look; maximizes natural light | Can be good or poor depending on the glazing and sealing | Limited ventilation; often combined with operable windows. |
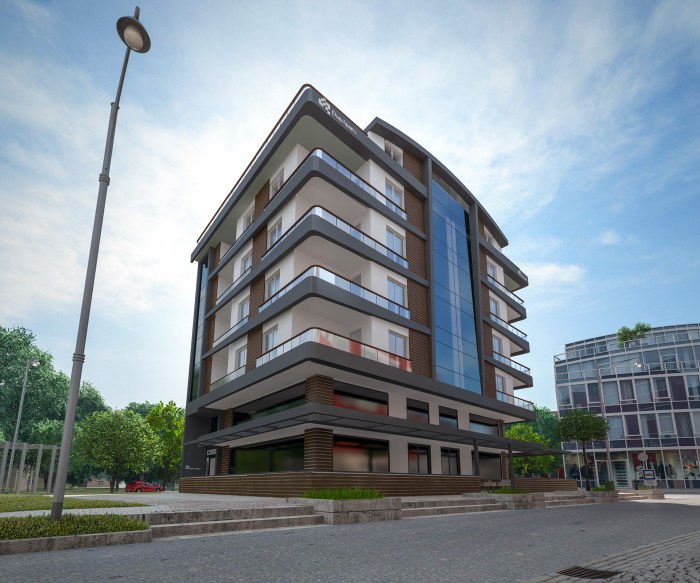
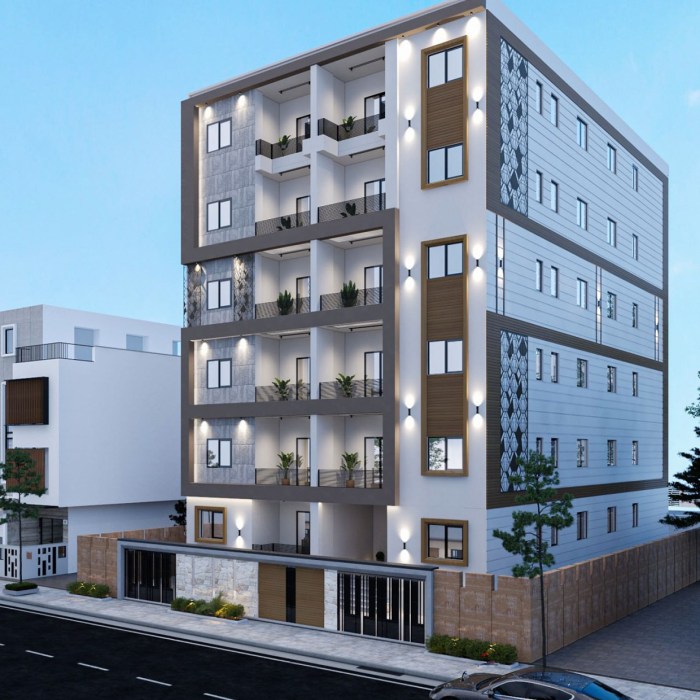
Adu Exterior Design

Source: behance.net
Designing the exterior of an accessory dwelling unit (ADU) requires careful consideration of its surroundings to ensure it complements, rather than clashes with, the existing environment and architectural style. A well-integrated ADU adds value to the property and the neighborhood, while a poorly designed one can detract from both. This section focuses on how site and context inform crucial design decisions.
Site Context and Seamless Integration
Harmonious ADU design begins with understanding the existing context. This includes analyzing the architectural styles of neighboring buildings, the prevalent colors and materials used, and the overall landscape character. For example, an ADU in a Victorian neighborhood might benefit from incorporating similar detailing, such as decorative trim, gables, and bay windows, using a palette of colors consistent with the area. Conversely, a modern ADU in a contemporary setting might feature clean lines, large windows, and a muted color scheme. Mimicking the roofline of the main house can also contribute significantly to a cohesive look. Imagine an ADU with a steeply pitched roof mirroring the main house’s roof, visually connecting the two structures and creating a sense of unity. Careful selection of materials, such as siding, roofing, and windows, can further enhance this integration. Using materials similar to those on the main house or neighboring buildings creates a sense of belonging and avoids a jarring contrast.
Site Orientation and Environmental Factors
Site orientation significantly impacts ADU exterior design. Understanding sun exposure and prevailing winds allows for optimizing energy efficiency and occupant comfort. South-facing walls (in the Northern Hemisphere) can be maximized for passive solar gain by incorporating large windows to capture sunlight during winter while minimizing window areas on the west side to reduce heat gain during summer afternoons. Conversely, in the Southern Hemisphere, north-facing walls should be prioritized for passive solar gain. Prevailing winds should also be considered when designing features like decks and patios, to ensure they are protected from harsh weather. For example, a sheltered patio facing away from the prevailing winds provides a comfortable outdoor space.
Sustainable Design Principles in ADU Exterior Design
Incorporating sustainable design principles is crucial for environmentally responsible ADU construction. Passive solar design, as mentioned above, reduces reliance on heating and cooling systems. Careful placement of windows and overhangs can control solar heat gain and loss. Water management strategies, such as rainwater harvesting for irrigation, greywater recycling, and the use of drought-tolerant landscaping, minimize environmental impact. Using locally sourced materials reduces transportation emissions while selecting energy-efficient building materials contributes to overall sustainability. The use of reflective roofing materials can significantly reduce heat absorption, lowering cooling loads. Consider using materials with high recycled content to further enhance sustainability.
ADU Exterior Design in Varied Climates
Climate significantly influences ADU exterior design choices. In hot and dry climates, light-colored exteriors and materials with high thermal mass help reflect sunlight and regulate internal temperatures. Features like shaded patios and overhangs provide relief from the sun. Conversely, in cold and snowy climates, dark-colored exteriors can absorb more solar heat, reducing heating loads. Materials with good insulation properties are crucial for maintaining interior warmth. Consider adding features like snow guards to prevent damage from heavy snow accumulation on the roof. Proper insulation and air sealing are vital in all climates, but especially crucial in extreme weather conditions. In coastal regions, the use of durable, weather-resistant materials is paramount to withstand wind, salt spray, and moisture.
Budgeting and Material Selection for ADU Exterior Design

Source: hsoubcdn.com
Planning the exterior of your Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) involves careful consideration of both aesthetics and budget. Choosing the right materials can significantly impact both the initial cost and long-term maintenance expenses. This section will guide you through creating a realistic budget and selecting cost-effective materials that still deliver a stunning look.
Cost-Effective Materials for ADU Exterior Design
Selecting materials that balance affordability and visual appeal is key to a successful ADU project. Prioritizing durability and low-maintenance options will save you money in the long run.
- Fiber Cement Siding: Offers a wood-like appearance with superior durability and resistance to rot, insects, and fire. It requires minimal maintenance and comes in a variety of colors and textures.
- Vinyl Siding: A budget-friendly option known for its ease of installation and low maintenance. While not as durable as fiber cement, it’s a good choice for those prioritizing affordability.
- Engineered Wood: Provides a natural look with improved durability compared to traditional wood. Look for treated options to increase resistance to moisture and insects.
- Metal Roofing: A long-lasting and low-maintenance roofing solution. While the initial cost might be higher than asphalt shingles, its longevity and resilience to weather damage often outweigh the upfront expense.
- Concrete or Paver Patios: These durable options require minimal maintenance and can withstand heavy use. They offer a clean, modern aesthetic.
Long-Term Maintenance Costs of Exterior Materials
Understanding the long-term maintenance needs of different materials is crucial for accurate budgeting.
| Material | Maintenance Requirements | Estimated Annual Maintenance Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Wood | Regular painting or staining, occasional repairs | $200 – $500 |
| Vinyl | Minimal cleaning, occasional repairs | $50 – $100 |
| Fiber Cement | Periodic cleaning, occasional repairs | $100 – $200 |
| Metal Roofing | Minimal maintenance, occasional cleaning | $50 – $100 |
Note: These are estimated costs and can vary depending on factors such as climate, size of the ADU, and the frequency of maintenance.
Creating a Detailed ADU Exterior Design Budget
A well-structured budget is essential for staying on track. Break down costs into categories:
- Materials: Include detailed pricing for siding, roofing, windows, doors, trim, paint, and landscaping.
- Labor: Factor in the cost of contractors for installation, painting, and other necessary work. Obtain multiple quotes for accurate cost comparisons.
- Permits and Inspections: Allocate funds for building permits and inspections required by your local authorities.
- Contingency: Include a buffer (10-15% of the total cost) to cover unexpected expenses.
Three ADU Exterior Designs with Varying Budgets
- Budget-Friendly Design (approx. $15,000 – $25,000): This design utilizes vinyl siding for its affordability and ease of maintenance. A simple gable roof with asphalt shingles is used. Landscaping is minimal, focusing on functionality and low-maintenance plants. The overall aesthetic is clean and modern, emphasizing practicality.
- Mid-Range Design (approx. $25,000 – $40,000): This design incorporates fiber cement siding for increased durability and a more upscale appearance. A more complex roofline might be included, potentially with metal roofing accents. Landscaping includes a combination of functional and aesthetically pleasing elements. The design incorporates a mix of modern and traditional elements.
- Luxury Design (approx. $40,000+): This design features high-end materials such as cedar or engineered wood siding, a sophisticated roof design with high-quality metal roofing, and custom detailing. Extensive landscaping with mature plants and hardscaping elements completes the luxurious look. The design emphasizes craftsmanship and unique architectural details.
Regulations and Permits for Adu Exterior Design

Source: idei.club
Building your Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) involves more than just picking out paint colors and siding. Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for a smooth and legal construction process. Understanding local building codes, obtaining necessary permits, and complying with HOA rules are all essential steps to avoid delays, fines, and potential legal issues.
Common Regulations and Building Codes Impacting ADU Exterior Design
Building codes are a set of rules that govern the construction and safety of buildings, including ADUs. These codes vary by location (city, county, and even state), so it’s essential to check with your local building department for specific requirements. Common regulations affecting ADU exterior design often include setbacks (minimum distances from property lines), height restrictions, roof pitch limitations, and material specifications (e.g., fire-resistant materials near property lines). Many jurisdictions also have design guidelines that influence aesthetic aspects like color palettes, architectural styles, and overall visual compatibility with the main house and neighborhood. These guidelines aim to maintain neighborhood character and curb appeal. For example, a historic district might have strict guidelines regarding the architectural style of new structures, potentially limiting your choices for ADU exterior design.
Obtaining Necessary Permits for ADU Construction
The permitting process typically involves submitting detailed plans and specifications of your ADU to your local building department. These plans must meet all applicable building codes and regulations. The review process can take several weeks or even months, depending on the complexity of the project and the workload of the building department. Once approved, you’ll receive a building permit, allowing you to begin construction. Failing to obtain the necessary permits before starting construction can lead to significant delays, fines, and even the need to demolish work already completed. The specific requirements for permit applications vary by location but typically include architectural plans, structural calculations, and details on all materials used.
Implications of HOA Regulations on ADU Exterior Design Choices
If your property is part of a homeowner’s association (HOA), their regulations can significantly impact your ADU exterior design choices. HOAs often have strict rules regarding exterior aesthetics, including color schemes, roofing materials, landscaping, and even the style of windows and doors. Before starting your ADU project, review your HOA’s covenants, conditions, and restrictions (CC&Rs) carefully. These documents will articulate the specific rules you must adhere to. It’s advisable to submit your ADU plans to the HOA for approval well in advance of submitting them to the building department. Disputes with the HOA can lead to significant delays and legal challenges, so proactive communication and adherence to their regulations are key. For example, an HOA might prohibit certain colors or require specific architectural styles, limiting your options.
Step-by-Step Guide for Navigating the Permitting Process for an ADU Exterior Renovation
- Research Local Regulations: Begin by contacting your local building department to obtain a complete list of all applicable building codes and regulations about ADUs.
- Develop Detailed Plans: Create comprehensive plans for your ADU exterior renovation, including detailed drawings, material specifications, and any necessary calculations. This should include all aspects of the exterior, from siding and roofing to windows and doors.
- Submit Permit Application: Submit a complete permit application to your local building department, including all required documentation and fees. This typically involves architectural plans, structural engineering calculations (if needed), and other supporting documents.
- Address Plan Review Comments: The building department will review your plans. If they have any comments or require revisions, promptly address these concerns and resubmit your application.
- Obtain Permits: Once your plans are approved, you’ll receive your building permits. Ensure that all permits are properly displayed at the construction site.
- HOA Approval (if applicable): If you have an HOA, obtain their approval before commencing construction. This might involve submitting your plans for review and gaining written consent.
- Construction: Begin construction after obtaining all necessary permits and approvals. Maintain accurate records of all work performed.
- Final Inspection: Schedule a final inspection with the building department upon completion of the construction to ensure compliance with all codes and regulations.
Final Review

Source: behance.net
Designing your ADU’s exterior is a rewarding process that allows you to blend aesthetics with functionality. By carefully considering architectural style, materials, landscaping, and local regulations, you can create a beautiful and functional space that enhances your property value and seamlessly integrates with its surroundings. Remember to prioritize sustainability and energy efficiency, and don’t be afraid to get creative! With careful planning and attention to detail, your ADU can become a stunning and valuable addition to your home.